1.
|
What is the colour code for a 47k resistor? |
|
|
2.
|
What is the value of the following resistor:
orange-white-yellow-gold
|
|
|
3.
|
Two10k resistors are connected as shown:
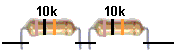
What is the combined resistance?
|
|
|
4.
|
What is the value of this resistor:
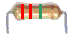
|
|
|
5.
|
What is the value of this combination:
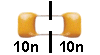
|
|
|
6.
|
Two resistors are placed in series to:
|
|
|
7.
|
Which set of resistors are found in the standard
5% range:
|
|
|
8.
|
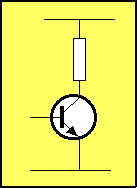 In the diagram
on the left, when In the diagram
on the left, when
the voltage on the base rises
(i.e: the current into the base
increases) what happens to
the voltage on the collector:
|
|
|
9.
|
The transistor-type in question 8 is:
|
|
|
10.
|
The input line in question 8 is:
|
|
|
11.
|
From Question 8, we can say:
|
|
|
12.
|
The resistor connected to the collector is
called:
|
|
|
13.
|
Three features of a resistor are:
|
|
|
14.
|
A Resistor and Capacitor in series is called:
|
|
|
15.
|
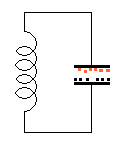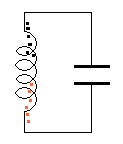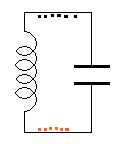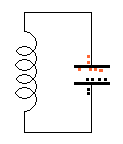 The
animation on the left demonstrates: The
animation on the left demonstrates:
|
|
|
16.
|
The arrows in the animation in question 15
represent:
|
|
|
17.
|
The natural waveform produced by a Tank Circuit
is:
|
|
|
18.
|
The characteristic voltage-drop across a red LED is:
|
|
|
19.
|
Two 100R resistors in parallel produce a
resistance:
|
|
|
20.
|
When a transistor "turns-on," the
resistance between the collector and emitter terminals:
|
|
|
21.
|
Two 100n capacitors in parallel produce a capacitance:
|
|
|
22.
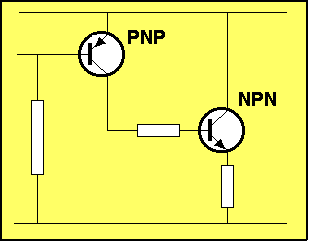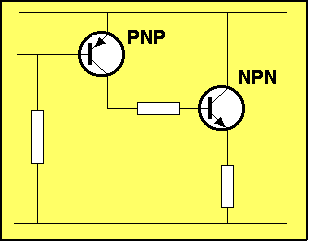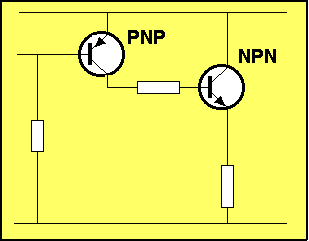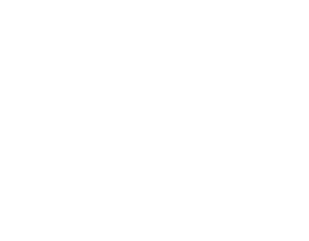
|
For the animation below, the resistor connected to the input of the first
transistor is
reducing in value.
This has the effect of:
|
|
|
|
|
23.
|
The animation above shows the NPN transistor rising. This is a
diagrammatical way of showing the transistor is:
|
|
|
24.
|
For the animation below, as the voltage on the
input rises, the output voltage:
|
|
|
|

|
25.
|
For the animation above, the input and output
voltages are:
|
|
|